Brain Imaging Behav. 2014 Jun;8(2):208-16. doi: 10.1007/s11682-014-9296-x. Epub 2014 Apr 22.
Chouinard-Decorte F1, McKay DR, Reid A, Khundrakpam B, Zhao L, Karama S, Rioux P, Sprooten E, Knowles E, Kent JW Jr, Curran JE, Göring HH, Dyer TD, Olvera RL, Kochunov P, Duggirala R, Fox PT, Almasy L, Blangero J, Bellec P, Evans AC, Glahn DC.
Author information
- McConnell Brain Imaging Centre, Montreal Neurological Institute, McGill University, Montreal, QC, H3A 2B4, Canada.
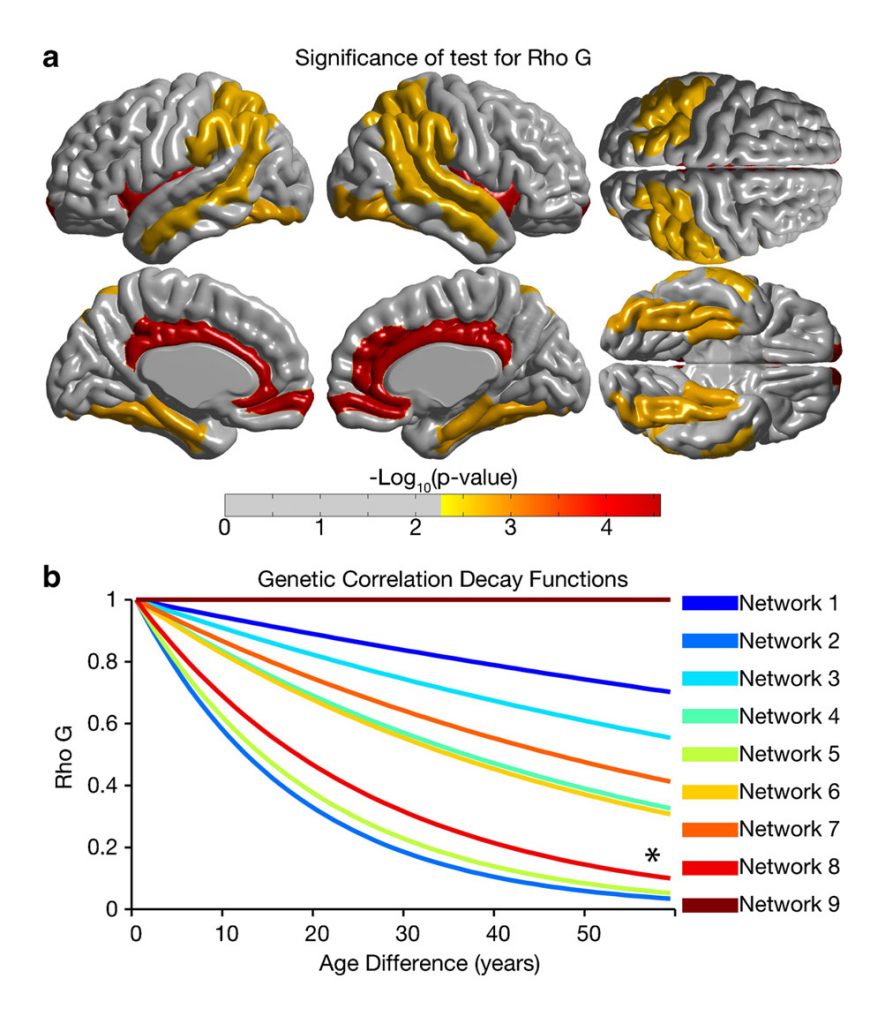
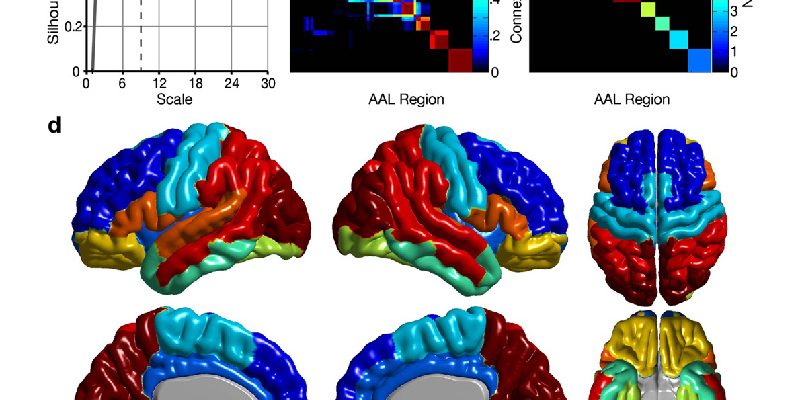
It is now well established that regional indices of brain structure such as cortical thickness, surface area or grey matter volume exhibit spatially variable patterns of heritability. However, a recent study found these patterns to change with age during development, a result supported by gene expression studies. Changes in heritability have not been investigated in adulthood so far and could have important implications in the study of heritability and genetic correlations in the brain as well as in the discovery of specific genes explaining them. Herein, we tested for genotype by age (G ×A) interactions, an extension of genotype by environment interactions, through adulthood and healthy aging in 902 subjects from the Genetics of Brain Structure (GOBS) study. A “jackknife” based method for the analysis of stable cortical thickness clusters (JASC) and scale selection is also introduced. Although additive genetic variance remained constant throughout adulthood, we found evidence for incomplete pleiotropy across age in the cortical thickness of paralimbic and parieto-temporal areas. This suggests that different genetic factors account for cortical thickness heritability at different ages in these regions.
PMID:24752552 | PMCID:PMC4205107 | DOI:10.1007/s11682-014-9296-x
Supplemental information
-
Publication types
MeSH terms
- Adolescent
- Adult
- Aged
- Aging/genetics*
- Aging/pathology*
- Cerebral Cortex/pathology*
- Family
- Female
- Genetic Pleiotropy
- Hispanic Americans
- Humans
- Image Processing, Computer-Assisted/methods
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging/methods
- Male
- Middle Aged
- Organ Size
- Phenotype
- Young Adult
Grant support
- R01 EB015611/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- MH083824/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MOP 37754/Canadian Institutes of Health Research/Canada
- R01 MH078111/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH59490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH059490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH078143/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH059490/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH083824/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH078111/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- MH0708143/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
More Resources